True/False
Indicate whether the sentence or statement is true
or false.
|
|
| 1. | When
a ball is rising upward after you toss it vertically, the net force on the ball is equal to the
force of gravity on the ball.
|
|
| 2. | You
pull horizontally on a rope, attached firmly to a hook on the wall, with a force of magnitude 16 N.
If you pull horizontally with a force of the same magnitude on a string held firmly by a friend,
the magnitude of the tension in the string is 32 N.
|
|
| 3. | A
grocery cart, at rest on a level floor, experiences a normal force of magnitude 155 N. You push on
the cart handle with a force directed at an angle of 25° below the horizontal. The magnitude
of the normal force is now less than 155 N.
|
|
| 4. | Snow
conditions are identical throughout the ski valley in Figure 1. The coefficient of kinetic
friction between a skier’s skis and the snow is 0.18 when the skier is travelling down the one
side of the valley. As the skier moves up the other side of the valley, the coefficient of kinetic
friction exceeds 0.18 because gravity is acting against the skier’s
motion.
Figure 1
|
|
| 5. | It
is impossible for an object to be travelling eastward while experiencing a westward net
force.
|
|
| 6. | It
is possible for the sum of three vector forces of equal magnitude to be zero.
|
|
| 7. | Static friction is always greater than kinetic friction.
|
|
| 8. | One possible SI unit of weight is the kilogram.
|
|
| 9. | When
you are standing at rest on the floor, there are two action-reaction pairs of forces
involved.
|
|
| 10. | Viscosity and air resistance are both types of friction involving
fluids.
|
|
| 11. | Fictitious forces must be invented to explain observations whenever the chosen
frame of reference is in motion.
|
Multiple Choice
Identify the
letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
|
|
| 12. | A person of
mass 65 kg is ascending on an escalator at a constant velocity of 2.5 m/s [22° above the
horizontal]. The magnitude of the net force acting on the person is a. | 0
N | b. | 6.4  102 N 102 N | c. | 5.9  102
N 102
N | d. | 2.4  102 N 102 N | e. | 1.6  102
N 102
N | | |
|
|
| 13. | On a windy
day, a quarterback throws a football into the wind. After the football has left the
quarterback’s hand and is moving through the air, the correct list of the force(s) acting on the
football is a. | a force from the throw
and the downward force of gravity | b. | a force from the throw, a force exerted by the air, and the downward
force of gravity | c. | a force exerted by the air and a force from the
throw | d. | a force exerted by the air and the downward force of
gravity | e. | the downward force of gravity | | |
|
|
| 14. | A skier of
mass m is sliding down a snowy slope that is inclined at an angle  above the
horizontal. The magnitude of the normal force on the skier is above the
horizontal. The magnitude of the normal force on the skier is a. | mg tan 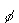 | b. | mg cos 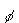 | c. | mg sin 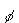 | d. | mg | e. | zero | | |
|
|
| 15. | A soft-drink
can is resting on a table. If Earth’s force of gravity on the can is the action force, the
reaction force is a. | an upward normal force
exerted by the table on the can | b. | a downward gravitational force exerted by Earth on the
table | c. | a downward normal force exerted on the table by the
can | d. | an upward force of
gravity on Earth by the can | e. | none of these | | |
|
|
| 16. | The
coefficients of friction between a box of mass 9.5 kg and the horizontal floor beneath it are
mS = 0.65 and
mK = 0.49.
The box is stationary. The magnitude of the minimum horizontal force that would suffice to set the
box into motion is a. | 93 N | b. | 61 N | c. | 46 N | d. | 6.2 N | e. | 4.7 N | | |
|
|
|
For questions 17 to 21, refer to Figure 2.
Figure 2
Two dynamics carts, one
a single cart of mass 1.0 kg, the other a double cart of mass 2.0 kg, each with essentially
frictionless wheels, are in contact and at rest. The compression spring on the single cart is
suddenly released, causing the cart to exert an average force of 2.0 N [E] on the double cart for
0.50 s.
|
|
| 17. | During the
time interval that the spring acts on the double cart, the force exerted by the double cart on the
single cart is a. | 2.0 N
[W] | b. | 0.0
N | c. | 2.0 N
[E] | d. | 4.0 N
[W] | e. | 4.0 N
[E] | | |
|
|
| 18. | During the
spring interaction, the net force acting on the single cart is a. | 4.0 N
[W] | b. | 2.0 N
[W] | c. | 2.0 N
[E] | d. | 4.0 N
[W] | e. | zero | | |
|
|
| 19. | During the
interaction, the acceleration of the double cart is a. | 0.33 m/s2
[E] | b. | 1.0 m/s2
[E] | c. | 3.0 m/s2
[E] | d. | 0.50 m/s2
[E] | e. | 2.0 m/s2
[E] | | |
|
|
| 20. | The velocity
of the double cart exactly 0.20 s after the compression spring is released is a. | 0.25 cm/s
[E] | b. | 1.0 cm/s
[E] | c. | 4.0 cm/s
[E] | d. | zero | e. | less than 0.25 cm/s [E], but greater than
zero | | |
|
|
| 21. | After the
spring interaction is complete and the carts are separated, the net force acting on the single cart
is a. | 19.6 N
[down] | b. | 2.0 N [W] | c. | 19.6 N [up] | d. | the vector sum of 19.6 N [down] and 2.0 N
[W] | e. | zero | | |
|